NodeJS → services readmongo_service, dummy_service
asynchronous event-driven
| As an asynchronous event-driven JavaScript runtime, Node.js is designed to build scalable network applications. |
Almost no function in Node.js directly performs I/O, so the process never blocks. Thanks to this, scalable systems is very reasonable to be developed in Node.js.
| Node.js is similar in design to, and influenced by, systems like Ruby’s Event Machine and Python’s Twisted. |
Node.js takes the event model a bit further. It presents an event loop as a runtime construct instead of a library.
In other systems, there is always a blocking call to start the event-loop.
Typically,
-
behavior is defined through callbacks at the beginning of a script,
-
and at the end a server is started through a blocking call like EventMachine::run().
|
In Node.js, there is no such start-the-event-loop call.
|
threads
Node.js being designed without threads doesn’t mean you can’t take advantage of multiple cores in your environment.
Child processes can be spawned by using our child_process.fork() API, and are designed to be easy to communicate with.
| Built upon that same interface is the cluster module, which allows you to share sockets between processes to enable load balancing over your cores. |
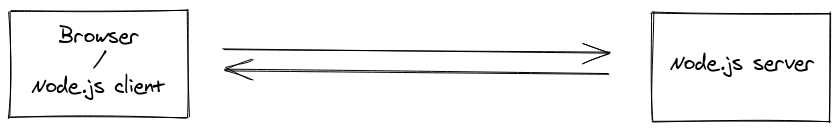
socket.io
Socket.IO is a library that enables real-time, bidirectional and event-based communication between the browser and the server.
It consists of:
-
a Node.js server: Source | API
-
a Javascript client library for the browser (which can be also run from Node.js): Source | API
express
Express is a minimal and flexible Node.js web application framework that provides a robust set of features for web and mobile applications.
Fast, unopinionated, minimalist web framework for Node.js